FlexDoc/XML - XSDDoc (XML Schema Documentation Generator)
- What is FlexDoc/XML XSDDoc?
- What you can generate with it
- What is processed/documented
- Documentation Features
- Possibility of unlimited customizations
- Getting Started
- Licensing
1. What is FlexDoc/XML XSDDoc?
A powerful XML Schema documentation generator that will help you to create a unified HTML or RTF documentation (with XSD diagrams) for any number of XML schema files.It is implemented in the form of «XSDDoc» template set for FlexDoc/XML.
- FramedDoc.tpl to generate framed HTML documentation
- SingleDoc.tpl to generate single-file both HTML and RTF documentation
'XSDDoc' subdirectory of FlexDoc/XML
archive or installation: {flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc
It is ready to use. Please read Getting Started!
2. What you can generate with it
Framed HTML Documentation
Using FramedDoc.tpl main template, you can generate a multi-framed HTML documentation by any number of W3C XML Schema definition (XSD) files. It looks similar to JavaDoc and provides most detailed and easily accessible information about all XML schema components as well as any interconnections between them.Here you can see some samples of such a documentation (click on a screenshot to view the real HTML):
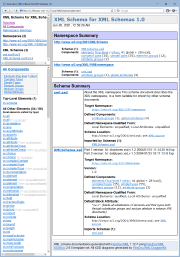 |
 |
The following functionality is supported:
-
Generation of file/page types:
- Basic Content Pages
- Cross-Reference Pages
- Support Files
Single-File Documentation
SingleDoc.tpl is another main template that generates the entire XML schema documentation as a single file/document, which can be in any supported output formats (primarily HTML and RTF).HTML Documentation
 With SingleDoc.tpl main template and the output format set to «HTML»,
you can generate a single-file HTML documentation. On the left is a demo documentation generated in that way (click on the screenshot to view HTML).
With SingleDoc.tpl main template and the output format set to «HTML»,
you can generate a single-file HTML documentation. On the left is a demo documentation generated in that way (click on the screenshot to view HTML).
RTF Documentation
Using SingleDoc.tpl main template with the output format set to «RTF», you can generate a single-file RTF documentation by any number of W3C XML Schema definition (XSD) files. It is built of the same basic blocks as the framed HTML documentation (which are actually generated by the same subtemplates) with a few additional features.These screenshots show pages of a demo RTF documentation (click to enlarge):
 |
 |
 |
 |
-
Main Sections (click on each link to see a corresponding screenshot):
-
Table Of Contents –
the actual table of contents is generated by MS Word according to the special
{TOC}field inserted in the RTF file - Overview Summary
- All Component Summary
- Namespace Overview - generated for each namespace
- Component Detail: Elements, Complex Types, Simple Types, Element Groups, Global Attributes, Attribute Groups
- Schema Overview – generated for each XML schema
- XML Namespace Bindings – a reference table to quickly find which namespace prefixes are bound which namespace URIs according to schema sources (those prefixes also appear in the documentation as a part of each XML qualified name).
-
Table Of Contents –
the actual table of contents is generated by MS Word according to the special
-
Page Header/Footer
- The page header shows the information about the current section, the footer - the documentation short title and the current page number.
-
Page Number References
-
Although the generated RTF includes hyperlinks (similar to those in HTML), they have no use in the printed form.
So, many hyperlinks are supplemented with the page number of the link's target shown like:
link text
[page number]
-
Although the generated RTF includes hyperlinks (similar to those in HTML), they have no use in the printed form.
So, many hyperlinks are supplemented with the page number of the link's target shown like:
link text
-
Rendering of HTML/XHTML tags in XSD annotations / template parameters
-
You can use XHTML tags in your XSD annotations (see below)
to format the text, define lists and tables, include images etc.
Equally, HTML tags can be used in some titles and descriptions passed via template parameters.
Although RTF is incompatible with HTML, all of the specified HTML/XHTML markup will be rendered with the appropriate formatting features of RTF (including lists, tables and insertion of images).
-
You can use XHTML tags in your XSD annotations (see below)
to format the text, define lists and tables, include images etc.
Equally, HTML tags can be used in some titles and descriptions passed via template parameters.
- Selectively forcing to start from a new page the documentation sections of particular types
PDF Documentation
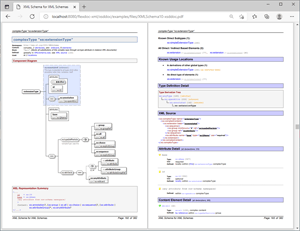
FlexDoc/XML currently generates no PDF directly. However, you can produce quite decent PDF from RTF using some converters. Here is an example of the XML schema documentation in PDF format created in that way (click on the screenshot to see/download the PDF file, 7.7 MB):3. What is processed/documented
Any number of input XSD files
- Any number of initially specified input XML schema (XSD) files.
- Processing and documenting (correctly and reliably!) huge XML schemas containing thousands of components.
All referenced XSD files
-
Correct processing of all
<xs:import>,<xs:include>,<xs:redefine>elements found across all involved XSD files. - Automatic loading and processing (i.e. inclusion in the documentation scope) all directly/indirectly referenced XSD files.
You just need to specify only the root XSD files of your project. Everything referenced from them will be loaded automatically!
Any XML schema design patterns
Like a single XML schema describes the structure of infinite number of XML files, the structure of the same XML file could be described by a great (potentially infinite) number of XML schemas. All of those XML schemas would differ from each other by ways of how they are designed. Those ways are called XML schema design patterns. Some of them were given even special names: chameleon, russian doll, salami slice, venetian blind, etc.When you design a schema, you definitely use some of those design patterns, even when you haven't heard of them. Simply, in that case you reinvent the pattern by yourself. When a schema is generated by some tool, it always follows a certain pattern.
So, how do all those design patterns differ from one another in respect of documenting them? Or asking it otherwise, what might be common? If you look closely into this, you could notice that all XML schema design patterns come down to a few specifics, all of which can be addressed by a single documentation approach:
| Design Pattern Specific | How It's Handled |
|---|---|
| The entire XML schema is broken into a number of XSD files, some of which import/include others. |
You don't need to do anything special about this.
Both <xs:import> and <xs:include> XSD elements
are supported. All referenced schemas will be automatically loaded and documented.
Moreover, using template parameters: you can even specifically disable documenting of imported/included schemas (even though they will be processed still). |
| There are several XSD files and some of them redefine certain components declared within others. |
That is done using <xs:redefine> XSD elements, which are processed/documented by XSDDoc very well!
See Also: Documenting of redefinitions |
| Some elements are declared locally. Such elements may share the same name, yet have different content models. Others may be absolutely identical (with equal names and based on the same global type), yet declared separately in numerous locations. |
If you document all of that straight (which is actually what all other known to us XML schema doc-generators always do!),
in certain cases you may get in your XML schema documentation a mess made of numerous repeating local element names,
in which it could be difficult to find some useful information.
XSDDoc provides two ways of dealing with that problem: |
| Locally declared elements are used everywhere instead of attributes to hold simple data. | Again, if you document it straight, various navigation lists and element summaries will get overwhelmed by insignificant local elements, in which you may have trouble to find what you need. XSDDoc provides a remedy to deal with this too, by documenting local elements in two ways: globally and locally. |
| There are groups of globally declared elements referenced across the schema via few abstract elements representing any element in a group. |
Such groups of elements, called substitution groups, are specifically recognized and processed/documented by XSDDoc. See Also: Documenting of substitution groups |
| The order in which elements/attributes are declared is important. |
Using the following template parameters you can preserve
the original ordering of your elements/attributes at various locations of the documentation:
|
| XML schema declares a possible root XML element that needs to be highlighted in the documentation. |
In general, the W3C XML schema specification
provides no functionality to assign which of the XML elements declared in XML schema must be
the root of any XML document that complies with that schema.
However, in many concrete situations, such an intention very much exists and needs to be documented somehow. To solve that problem, we have introduced a concept of top-level elements. Top-level element is the one, which satisfies the following conditions:
Typically, very few such elements can be found in an XML schema (possibly one or two per a namespace). Using the template parameter: you can separate the top-level elements and thereby highlight what you intended to be the main element in your schema (e.g.<xs:schema> in XML schema for XML schemas).
If the separation of top-level elements doesn't work for you, alternatively, you can declare the root element the first in your XML schema. Further, when you generate documentation for that XML schema, unselect the template parameter: That will preserve the original order of element declarations in the documentation.If your XML schema is broken into several XSD files, specify the one of them that contains the root element declaration to be processed the first by the generator and unselect the parameter: That will ensure that the root element gets on the top of various navigation lists and summaries, which will highlight its special role. |
Joint documenting of conflicting XML schemas
Conflicting XML schemas are those that define the same components (that is with the same local name and in the same namespace). For instance, different versions of some your XML schema project will likely contain conflicting XML schemas.Since the version 2.6.0, XSDDoc is able to document correctly any number of conflicting XML schemas!
-
Among all XML schemas initially specified for documenting, the main schemas are identified.
These are the schemas that are not referenced from other schemas.
Here, schema reference is any of the elements:
<xs:import>,<xs:include>and<xs:redefine>. Note that any conflicting schemas, if they are correct indeed, cannot reference to each other (both directly and indirectly)! - The main schemas break everything into several domains adding to each name a sort of extra "namespace". This makes possible to resolve global component references only within a particular main schema domain, which the given reference belongs to.
-
Some XML schemas involved here may be those referenced from several conflicting schemas simultaneously.
These must be some library schemas valid in all cases. For instance:
-
<xs:import namespace="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace" schemaLocation= "http://www.w3.org/2001/xml.xsd"/>
-
-
In the case of multi-file framed HTML documentation,
if the names of conflicting XML schema files are repeating too,
the components of those schemas will still be documented in separate subdirectories.
Normally, such a subdirectory name is derived from the name of the XML schema file.
If that name duplicates another schema's name, it will be extended with a numeric suffix so as to make
the subdirectory unique. For example:
-
{xsddoc}/schemas/XMLSchema_xsd/
{xsddoc}/schemas/XMLSchema_xsd_1/
-
XHTML tags in your descriptions/annotations
Below is a demo of what can be achieved using XHTML markup in XML schema annotations. On the left you can see the XML source of an XML schema, whose annotations are heavily laden with XHTML markup (including insertion of images). The next is the framed HTML documentation generated by that schema (click on screenshots to see the actual HTML):
 |
 |
 |
 |
The last two screenshots show pages of the RTF documentation generated by that schema (click to enlarge). Here, you can also download a PDF converted from that RTF: HumanEvolution.pdf
See Also:
- FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | FAQ | Using HTML markup in annotations
- FlexDoc/XML | Features | Formatting | Processing of XHTML markup
Support of XML Catalogs
XML catalog(s) may be used in a large XML schema project to avoid referencing separate XSD files from each other by direct file names. You may also want to use an XML catalog when some XSD files involved in your project are located differently as they are specified in other XSD files.See also: FlexDoc/XML | Documentation | Generator | Input XML | XML Catalogs
4. Documentation Features
This section highlights some advanced features, which you rarely find in other documentation generators. That makes our tool so special!Highly navigable framed HTML documentation
The idea comes from Javadoc:
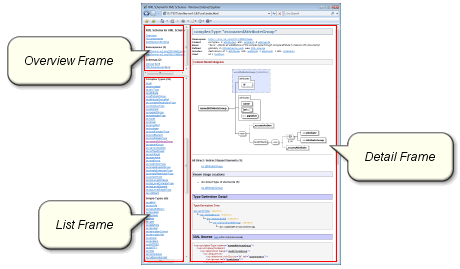
See Also: Framed HTML Documentation
Detail header & navigation bar
Here is the commented screenshot of the header & navigation bar inserted at the top of each detail page. The navigation bar is added also at the bottom. The screenshot links lead to the corresponding template parameters that control/specify the respective features:

Dynamic search functionality
 XSDDoc supports the dynamic search that works similar as in the modern Javadoc.
All identifiers like XSD component names, attributes etc. are indexed.
XSDDoc supports the dynamic search that works similar as in the modern Javadoc.
All identifiers like XSD component names, attributes etc. are indexed.
The dynamic Search-Box powered by JQuery UI can be embedded into the Navigation Bar at the top and bottom of each detail page as shown on the screenshot (click to view in full size).
The search-box is also available on the special Search Page that shows the search help and index statistics, which lists what exactly is indexed. The Search page hyperlinked from the Navigation Bar and the Overview Frame.
Related template parameter: Navigation | Search
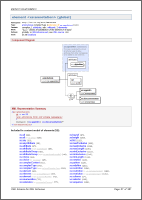
Dense layouts: more information in less space
 |
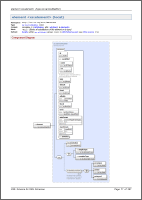 |
Using it, it is possible to generate such things as shown on the left screenshots (click to enlarge).
You may think: What's special here? Just yet another pages of some documentation... But they use four grid layouts! If that technique was not applied, the information printed on those pages would occupy 3-4 pages instead!
Abundance of cross-links
When you look at a documentation generated by our tool, you can see a lot of hyperlinks. Everything seems to be a hyperlink!Cross-links are produced by matching sets of special keys generated for both link source and destination. The keys represent actual data being linked. Their generation is specified in templates along with the generation of the corresponding pieces of output. In that way anything can be cross-linked together. At that, if a particular set of keys cannot be matched, an alternative set of keys can be specified as well. That means, when the primary target is absent, the link can go to some alternative location related to the link source.
For instance, when in a reproduced XML source the value of some attribute is the name of some XSD component, that value is linked to the component detail. But when the detail is absent, the link can go to a corresponding item in some component summary:In RTF documentation intended for printing, some cross-links can be emulated with page number references that appear in square brackets after the linked item, as visible in the above screenshot.
See Also: FlexDoc/XML | Features | Hypertext | Cross-Reference Links
Documenting of local elements
This XML Schema documentation generator possesses a unique capability to document all local elements defined in your XML schemas. In fact, we have never seen anything like this in any other software/tool supposed to generate XML schema documentation!What are local elements?
Local Elements are those element components that are defined locally within:- complex types (either global ones or defined anonymously within other elements)
- element groups (which are separate schema components that define whole bunches of elements arranged in specific complex models).
| Problem | Description/Solution |
|---|---|
| Locally declared elements are used everywhere instead of attributes to hold simple data. | Documenting them straight (together with global elements and local element with complex content) may result in that various navigation lists and summaries get overwhelmed by insignificant items. That may greatly reduce the clarity of the documentation and impede its navigation. |
| There are many element declarations with the same name but based on different types. |
Since the introduction of local elements in W3C XML Schema language, there is no strict relationship
between the element name and its type for the entire scope of the XML document.
Now, within the same XML document, you may find several different XML elements that although share the same name,
actually represent more or less different things and, therefore, may have different attributes and content.
It is clear that such equally named but essentially different local elements must be documented separately.
Solution: Adding extensions to local element names |
| Certain local elements share the same name and the same global type, yet are declared separately in numerous locations. |
In many cases local elements are declared very simply:
Solution: Unifying local elements by type |
Global and local documenting of local elements
Local elements can be documented simultaneously in three ways: globally, locally, in content model tables.The purpose of three ways of documenting is that some elements may be important to show up in various navigation lists, whereas others play a more subsidiary role and are better to be documented locally where they are defined/used. Yet others, particularly with predefined simple content, play effectively the role of attributes. So, some single row in a content model table will fully suffice for them. Exposing many insignificant elements in the navigation lists and summaries (along with the global elements or those with complex content) may blow out and overwhelm such lists and make them difficult to navigate.
As examples, here are three documentations generated for the same little XML schema (from “Sales Report” sample).
Global Documenting
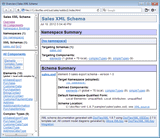 Global documenting of a local element means generating for it the full Component Documentation block/page with all possible details about the element.
In the case of framed HTML documentation, that page is loaded in the Detail Frame and the element will also appear in the
navigation lists shown in the documentation List Frame (on the left).
Global documenting of a local element means generating for it the full Component Documentation block/page with all possible details about the element.
In the case of framed HTML documentation, that page is loaded in the Detail Frame and the element will also appear in the
navigation lists shown in the documentation List Frame (on the left).
Which local elements are documented globally is controlled by the parameter group: Generate Details | Components | Elements | Local Elements
On the left screenshot is the XML schema documentation with all elements (both global and local) documented separately (globally). Click on the screenshot to view the doc.
Local Documenting
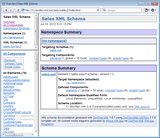 Local elements can be documented also locally together with their parent components where they are defined.
In that case, the local element is documented the same as attribute.
That documentation appears in the Content Element Detail section of the Component Documentation block/page
generated for the element's parent component and may contain fewer details.
Local elements can be documented also locally together with their parent components where they are defined.
In that case, the local element is documented the same as attribute.
That documentation appears in the Content Element Detail section of the Component Documentation block/page
generated for the element's parent component and may contain fewer details.
What is included in the Content Element Detail is controlled by the parameter group: Details | Component | Content Element Detail
On the left screenshot is the XML schema documentation, in which only global elements and local elements with complex type are documented separately. All local elements with simple content are documented locally. Such a documentation may appear tidier and easier to navigate. Click on the screenshot to view it.
Documenting inside Content Model Tables
 Local elements can be documented also along with the component's content model in a special Table Representation.
That is similar to local documenting but far more compact.
Each child element is described by a single row in that table, which in many cases is just enough to represent all to know about that element.
Local elements can be documented also along with the component's content model in a special Table Representation.
That is similar to local documenting but far more compact.
Each child element is described by a single row in that table, which in many cases is just enough to represent all to know about that element.
Click on the screenshot to view the XML schema documentation, in which only global elements and local elements with complex type are documented separately. All local elements with simple content are documented locally inside content model tables.
Adding extensions to local element names
Using local elements, you can define in an XML schema several element components with the same name but different content. That's OK to verify an XML file (for which XML schemas are typically used). But it creates a problem for documenting. Since the main purpose of the documentation is to show relations between components, all element components eventually surface globally. For instance, when you have a list of some element components that share particular properties, very likely it will include several local elements with the same name. If nothing is done about that, you will see repeating names in that list, which may look quite confusing. XSDDoc solves that problem by adding some extensions to the repeating element names, which make those elements unique. The extensions are generated according to:- The element's possible parent in an XML document (its containing element), when there can be only one of such
- The element global type (see also below)
- The XSD component, where the element is defined
 On this screenshot you can see how element name extensions look (the grey text).
On this screenshot you can see how element name extensions look (the grey text).
Related template parameter: Show | Element Name Extensions
Unifying local elements by type
When a single name is used for several element components that means they share something common. Sometimes that 'common' comes down to the element type. For instance, in many XML schemas instead of defining a single global element and reference to it from many locations, multiple identical local elements are declared like this:
You've got lots of local element components that define effectively the same thing. So, instead of flooding the documentation with repeating element names, why not to document all those local elements (with the same global type) as a single one? We shall call it unified local element and its name extension (when necessary) will be just the name of that global type.
Here's how it works:
 |
 |
Related template parameter: Generate Details | Components | Elements | Local Elements | Unify By Type
List of containing elements
When you look at details of an XSD element component (produced by any doc-generator), you will typically see which children an XML element represented by that component may have. But it is equally interesting to know the possible parents of an XML element! Specifically, the list of those XSD element components, whose content model includes the given one.
 Here is an example of such a list (click on the screenshot to see it within the documentation).
Here is an example of such a list (click on the screenshot to see it within the documentation).
Related template parameters:
- Details | Component | Related Components | Containing Elements
- Details | Component | Content Element Details | Containing Elements
Documenting of redefinitions
Redefinition of an XML schema is a type of its inclusion into another schema using<xs:redefine>
element, during which some components defined in the included schema may be replaced with equally named components however defined differently (redefined)
within the <xs:redefine> element. Those redefinitions are typically derived from the previous versions of the same components.
A component may be redefined any number of times (in different XML schemas calling one another through <xs:redefine> elements).
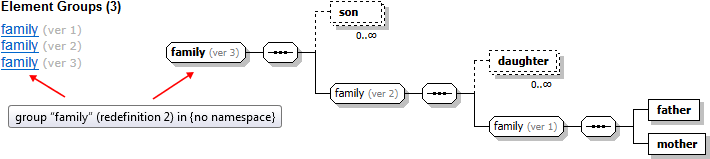
Each redefinition creates a new version of the component. XSDDoc documents all such versions (including the initial one). To distinguish them,
an extension is added to the component name showing the component version.
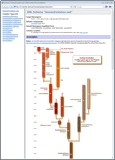
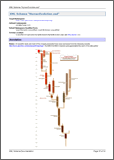
On the following composite screenshot you can see a 'family' element group redefined two times (all three versions in the same list on the left
and the diagram of the last version on the right):
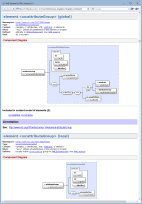
Documenting of substitution groups
Substitution group is a group of globally declared elements (called group members), each of which may substitute for the same element (called group head), specified in member element definitions withsubstitutionGroup attribute.
XSDDoc recognizes substitution groups and documents them both in the documentation (as member list, list of possible parents by substitution and so on) and on the diagrams (as a special branch with group member elements attached to the group head).
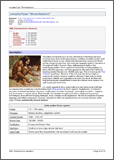
 On the screenshot (left) you can see the XML schema documentation, generated by an XML schema that uses substitution groups. Click on the screenshot to view it.
On the screenshot (left) you can see the XML schema documentation, generated by an XML schema that uses substitution groups. Click on the screenshot to view it.
Documenting of content model
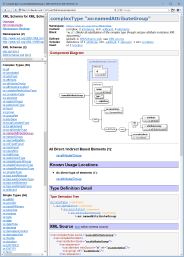
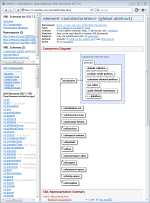
The complex content (i.e. possible attributes and child elements) described by the component can be represented in three different ways simultaneously: The simple content is fully documented as well with the Simple Content Detail.Component Diagram
Component diagram can be generated for elements, complexTypes and element/attribute groups.The diagram provides:
- A graphical view of the complex content represented by the component, including:
- All relevant attribute declarations
-
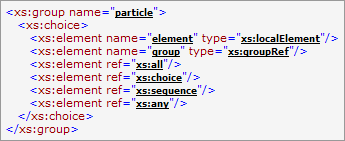
The content element model, which represents all possible combinations of child elements.
This includes also the depiction of all compositors (such as
<xs:sequence>,<xs:choice>,<xs:all>) and all model groups involved in building of that content model.
- The members of substitution groups, whose head element appears in the content model or is the main component itself.
- Some information about ancestor components: element type, base type, element/attribute groups.
- The annotations to everything above
- The properties of elements and attributes, which provided extra information such as the element/attribute type, content, facets, default value etc. Properties are displayed in the little grid embedded within the diagram node depicting the element/attribute.
- Most of things depicted on the diagrams are hyperlinked to the corresponding documentation detail.
All diagrams visible on this page and in all XSDDoc examples have been generated by DiagramKit.
The following screenshots are two diagrams of the same XSD component. On the left is the diagram with the element/attribute properties. On the right is the diagram without the properties. Click on the screenshots to see each diagram in full size within the corresponding documentation: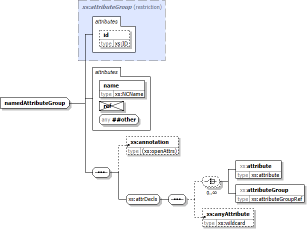 |
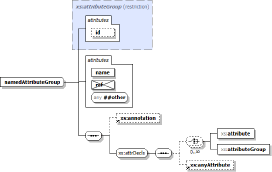 |
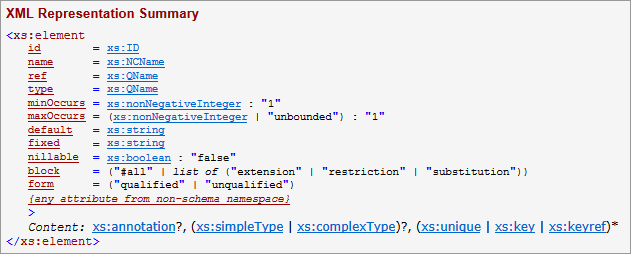
XML Representation Summary
XML Representation Summary section can be generated for each schema component. It provides a schematic text representation of all possible XML elements this component describes as well as how such elements may look in XML file. This includes:- The list of all possible attributes an XML element may have.
- The type and possible values for each attribute.
- The representation of the element content, which has two different forms for a simple and complex content.
- The element's simple content is represented in the form of a data type and possible values the element may enclose.
- The element complex content is represented with the use of extended Kleene operators (see below).
Content Element Models are represented using Kleene operators (the same as used in XML DTD) extended with two more operators to cover all situations allowed by W3C XML Schemas. The following table shows all operators used in Content Element Model representations:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| , | sequence |
| | | choice |
| () | grouping |
| ? | 0 or 1 times |
| + | 1 or more times |
| * | 0 or more times |
| Extended operators | |
| × |
The idea of this operator can be expressed by the formula:
|
| [n1, n2] |
General cardinality operator (n1 can be 0 or any number; n2 is any number or *).
It is used in those rare situations when Kleene cardinality operators (?, +, *) are not enough. For example:
|
Related template parameters: Details | Component | Component Model | XML Representation Summary
Table Representation
This is the third alternative way to represent the complex content defined by an XSD component – the most complete and easy to understand. It consists of two tables like shown on the following screenshots: Content Element ModelSuch Table Representations can also include the full or partial description of each attribute and content element. Thereby, they can be used as a light-weight compact documentation of those attributes and elements.
- Global & Local Elements
- Complex Types
- Element / Attribute Groups
Simple Content Detail
<xs:string> or
<xs:boolean>) or their lists.
In the case of XML elements, such data may represent the content of some element. In the case of attributes, it is the attribute value.
- XSD basic simple type
- Various restrictions specified with facets.
- The definition of a list
- The definition of a union (i.e. when several basic types or their lists may interchange)
- The default value
- Simple Content Representation (visible at the top in the box), which briefly shows how the datatype is related to the XSD basic simple types, their lists or unions.
- The details of the union(s), list(s) and restrictions along with their descriptions found in the corresponding XML schema annotations.
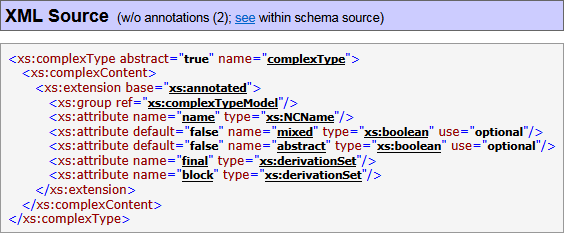
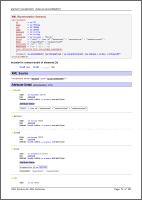
Documenting of XML source
The XML source of the whole XML schema file is included in the «Schema Source» page/block (see below on the left screenshot; click to view). Equally, the XML source defining a particular component can be included in «Schema Source» of «Component Documentation» (the right screenshot):
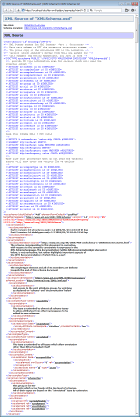 |
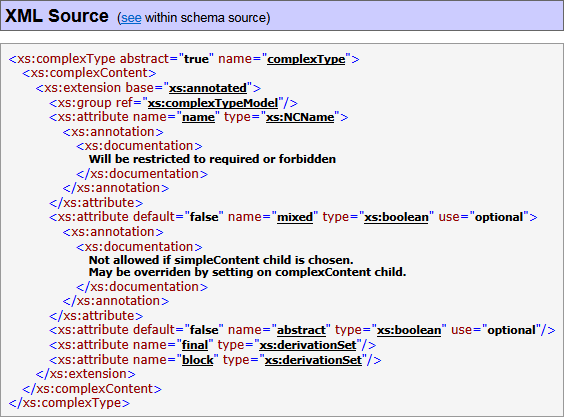 |
That XML source is actually reproduced from the DOM representation of the schema file. However, it closely follows the original one enriched with the following features:
- XML markup, tags, attribute names and values, XML comments and other XML source declarations are highlighted with separate colors
- All XSD component references in attribute values are hyperlinked to the corresponding «Component Documentation» (or any other details available in the documentation)
- The XML source of a particular component is hyperlinked to its location within the full XML schema source – the «see» link in the «XML Source» heading (visible on the right screenshot above).
-
It is also possible to remove from the reproduced XML source the entire
<xs:annotation>elements (which is controlled by “... | XML Source | Remove Annotations” parameters). Here is how the initial XML source fragment (above on the right) looks after removing its annotations:You may want to suppress
<xs:annotation>elements in the reproduced XML source when you use XHTML to format your annotations, because the XHTML markup elements may occupy too much space (so they will overwhelm anything else).
- FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | FAQ | Using HTML markup in annotations
- FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | Templates | Subtemplates | [lib/xml]
5. Possibility of unlimited customizations
Template parameters
Since all content and formatting of the generated documentation is programmed entirely in templates, the numerous options and switches, which normally control traditional documentation generators, now simply become template parameters.On the other hand, to avoid overwhelming the user with too many unimportant settings, many template parameters inherit or derive their default values from other top-level parameters. So, you actually need to change only a few of them. The entire parameter set is organized in a tree, which makes it easier to understand and navigate. That tree is displayed in the Parameter Inspector as shown below.
See Also: FlexDoc/XML | Documentation | Generator | Template Parameters
XSDDoc is controlled by ca. 500 parameters, which you can specify in Parameter Inspector invoked from the generator GUI (when you click «Params» button with one of the main templates selected):
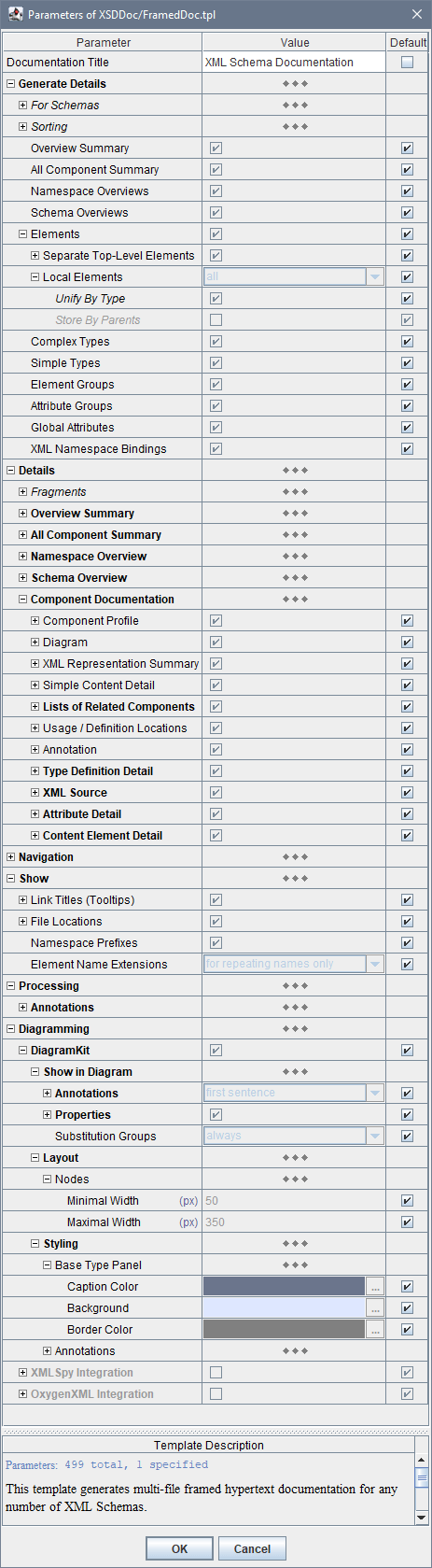
Alternatively, you can specify any template parameters through Java command line using -p option.
See Also:
Generator options
Generator options are more traditional things. They control particular features of the selected output generator (that is what is hardcoded in Java code).Generator options are separated from templates. They do not depend on the selected template as well as their settings are not used in templates at all. That's because templates are designed to be mostly independent of the particular output format. Only some general assumptions about the output format are accounted, for instance, whether it supports pagination and has page numbers.
Which particular generator options are available depends on the selected output format, which currently may be HTML, RTF and TXT (plain text). In the generator GUI, after you have selected the destination output format, you can click «Options» button, which will invoke Format Option Inspector. Here you can see all options available for the given format and specify them. This screenshot shows the HTML Option Inspector:

Alternatively, you can specify any generator options (along with template parameters) through Java command line using -o option.
See also: FlexDoc/XML | Generator | Output Formats
Using custom CSS styles
You can apply also your own CSS styles to change how the generated documentation looks.
 |
 |
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/templates/css/azure-theme.css
How to specify it is shown in the HTML Option Inspector screenshot above. You should set:
- Output | CSS | Generate named rules = all
- Output | CSS | Generate named rules | Custom rules file = Stylesheet file path name
Note that the possibility to use any CSS stylesheets is available only under the “FlexDoc/XML SDK” license (which covers the Template Designer).
See Also:- FlexDoc.XYZ | Documentation | Usage of CSS in generated HTML
- FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | Licensing | Full Licenses | FlexDoc/XML SDK
Modifying templates with Template Designer
If template parameters and CSS styles are not enough, you can modify the templates themselves using the Template Designer:
 Template Designer is a highly sophisticated GUI used to design/edit templates.
It represents the template both in the form template components,
which it is made of, and the output those components would generate.
Template Designer is a highly sophisticated GUI used to design/edit templates.
It represents the template both in the form template components,
which it is made of, and the output those components would generate.
This screenshot shows XSDDoc/templates/lib/content/tableRep.tpl template open in the Template Designer (click on the screenshot to see in full size).
That template generates the Table Representation section.
Template Designer is covered by the separate “FlexDoc/XML SDK” license, which you need to acquire along with “FlexDoc/XML XSDDoc” license, if you want to modify XSDDoc templates.
See Also:
- FlexDoc/XML | Features | Template-driven architecture
- FlexDoc/XML | Documentation | Designing Templates | Running Template Designer
- FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | Licensing | Full Licenses
- Licensing | Licensing of Templates | Custom Templates
6. Getting Started
You can try XSDDoc right now, without any registration! Just download FlexDoc/XML zip-archive and follow the instructions below.By default, everything will work in demo mode. You will be able to generate a reduced documentation (including diagrams) by any your input XSD files. If they are small enough, that will be actually the complete documentation, which you can use for free! For further details, see Licensing.
How to run XSDDoc?
This section was moved to FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | FAQ. Please follow the links to jump directly to the corresponding content:
How to include diagrams?
This section was moved to FlexDoc/XML | XSDDoc | FAQ | How to include diagrams?How to integrate with Ant/Maven/Docker?
A demo about that you can find in your FlexDoc/XML installation:{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run/ant/
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run/maven/
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run/docker/
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run_with_DiagramKit/ant/
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run_with_DiagramKit/maven/
{flexdoc-xml}/XSDDoc/run_with_DiagramKit/docker/
7. Licensing
Demo Mode
Once you have downloaded FlexDoc/XML archive, you can run XSDDoc immediately and see what it is. You don't need to request any trial and register anywhere!By default, everything will work in demo mode. It means that all your input XSD files will be fully processed, however fully documented will be only limited number of components. Component diagrams will be generated as well by any diagramming plugin you choose and as many as it's allowed by XSDDoc demo limits. What exactly the demo limits are depends on a particular main template (as well as some metrics).
If those limits are not reached, you will get the complete documentation. Otherwise, some content will be omitted and the message included saying which limits were exceeded. Anyway, the result documentation will be minimally distorted, to allow you to evaluate how everything will look under the full license. Any documentation generated in demo mode is yours. You may use it for free as you wish.
Template Designer will work in demo mode as well. You will be able to run it, investigate some functionality, but unable to save any created/modified templates.
See also: Licensing | Demo License
Trial License
The standard package of trial licenses (see below) unlocks full functionality of XSDDoc / DiagramKit / Template Designer. You will be able to evaluate how everything works, generate the complete documentation by all your XSD files. It will include all possible details (according to the settings specified in template parameters). All XSD diagrams will be generated as well.But there will be some limitations:
- All generated output documents will be specifically distorted by replacing some letters with shade ('░') characters (as well as contain special messages).
- Component diagrams will contain trial watermark.
- Any output documents or diagrams may be used only for evaluation of this software. Any other usage is prohibited!
- Trial license is limited to 30 days.
Then, you will be redirected to Try | Trial License page with “FlexDoc/XML” preselected in the «Product» field.
{flexdoc-xml}/lib/ directory (near 'flexdoc-xml.jar' file).
See Also:
- Licensing | Trial License
- Licensing | Licensing of Templates | Commercial Template Applications
- Licensing | Multiple Licenses
Full Licenses
The whole functionality described on this page is covered by three different full licenses:
| License | Description |
|---|---|
| FlexDoc/XML XSDDoc |
Unlocks all functionality implemented in XSDDoc templates.
In particular, you will be able to:
|
| FlexDoc/XML DiagramKit | Unlocks all functionality implemented in DiagramKit. Allows you to generate XSD diagrams and automatically insert them into documentation generated by XSDDoc (with the support of all possible diagram hyperlinks). |
| FlexDoc/XML SDK |
You need this license if you want to heavily customize the generated documentation (e.g. change some colors, fonts, layouts, look & feel, add new functionality etc).
In particular, this license covers:
Please note that neither commercial template applications themselves (e.g. XSDDoc) nor diagramming plugins are covered by this license! |
See Also:
Which Licenses You Need - Use Cases
You don't have to purchase all full licenses listed above – only those required for your particular goal:
| Your goal | The license(s) you need |
|---|---|
You can order any combination of those licenses starting from Store page.